Identification of Cashmere Fibers
Quality Labeling of Textile Products
Cashmere is an expensive animal fiber because of the rarity. Mislabeling of cashmere products blended with other cheaper animal fibers has been repeatedly reported. In Japan, the products of animal fibers are required to be labeled according to the Household Goods Quality Labeling Act. The Japan Fair Trade Commission issued exclusion orders against four traders because of the mislabeling of blended fabric items as cashmere from 2007 to 2008. The official method for differential identification of animal fibers has been the visual judgment under a microscope. However, the increase of chemically-treated fibers is making it difficult to distinguish them by the current visual method.
Identification of Animal Fibers by Protein Analysis
The animal fibers consist mainly of proteins called keratins. Therefore, to analyze proteins contained in textiles is generally regarded as one of the most promising identification methods and the related studies have been conducted at universities or research institutes.
Mass spectrometry is commonly used as the method to analyze proteins stably. The general method includes that proteins are digested to peptides by trypsin to convert to smaller molecules to be suitable for detection in mass spectrometer.
The studies mainly focus on the methods using MALDI-TOFMS and LC/MS among the various types of mass spectrometers.
The method using MALDI-TOFMS is rapid and has high throughput. On the other hand, the instrument is expensive and has low quantitative capability.
The other method using LC/MS has therefore also been studied because of the lower price and the general versatility of the instrument. LC/MS has high quantitative capability and potential to calculate the blending ratio. On the other hand, the disadvantage is a long measurement time. However, it is expected that a measurement time will be shorten by the contribution of the development of ultra-high pressure LC.
- * MALDI-TOFMS: Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption /Ionization Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometer
- * LC/MS: Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer
Standardization of Identification Methods of Animal Fibers
The standardization of identification methods of animal fibers using MALDI-TOFMS and LC/MS was deliberated in ISO (International Organization for Standardization)/TC38 (Textiles)/WG22 (Composition and chemical testing). The standard consists of the following three parts.
(1) ISO 20418-1:2018 Textiles -- Qualitative and quantitative proteomic analysis of some animal hair fibres
-- Part 1: Peptide detection using LC-ESI-MS with protein reduction
(2) ISO 20418-2:2018 Textiles -- Qualitative and quantitative proteomic analysis of some animal hair fibres
-- Part 2: Peptide detection using MALDI-TOF-MS
(3) ISO 20418-3:2020 Textiles -- Qualitative and quantitative proteomic analysis of some animal hair fibres
-- Part 3: Peptide detection using LC-MS without protein reduction
NITE has been developing a practical identification method aiming for 1) using versatile LC/MS instruments, 2) shortening the time required for the identification and 3) simplifying the processing steps. The animal fibers consisting mainly of keratins are generally treated with denaturants or detergents because of its poor solubility. The denaturants or detergents in samples, however, often inhibit the LC/MS analysis, and the denaturation step takes longer time. Therefore, we developed the identification method without prior denaturation as described in Part 3 of the forthcoming ISO standard.
Standardization of Identification Method Developed by NITE
The identification method developed by NITE is being standardized not only by ISO but also by CEN (European Committee for Standardization) and more than 30 countries.
Development of Testing Method for Fiber Identification
The process for developing the testing method is outlined below.
- (1) Pretreatment of fibers
- Keratin, major component of animal fibers, is insoluble in neutral solvent such as water. To analyze keratin, digestion is needed both for the solubilization and for the analysis in mass spectrometer. To eliminate the denaturation step as described above, fiber samples were washed, crushed into fine powder, and directly digested by trypsin. Trypsin is the most frequently used proteolytic enzyme in protein analysis. The tryptic digest was dried in a vacuum.
- (2) Selection of candidate peptides for identification
- The resultant peptides were comprehensively analyzed by MALDI-TOFMS and ion trap LC/MS/MS. Thousands of peptides derived from keratin were identified and the peptides specific to each animal species were selected.
- (3) Determination of peptides for identification
- The selected specific peptides were further targeted in the measurement by the triple quadrupole LC/MS and validated for use in identification. For instance, even if the sequence of the peptide is specific to the targeted animal species, the peptide is unsuitable for identification in the event that a peptide in another species has the same molecular weight and close retention time by chance. A set of peptides for identification of each animal fiber has been thus determined from the selected peptides on the basis of the selectivity and the qualitative and quantitative reproducibility.
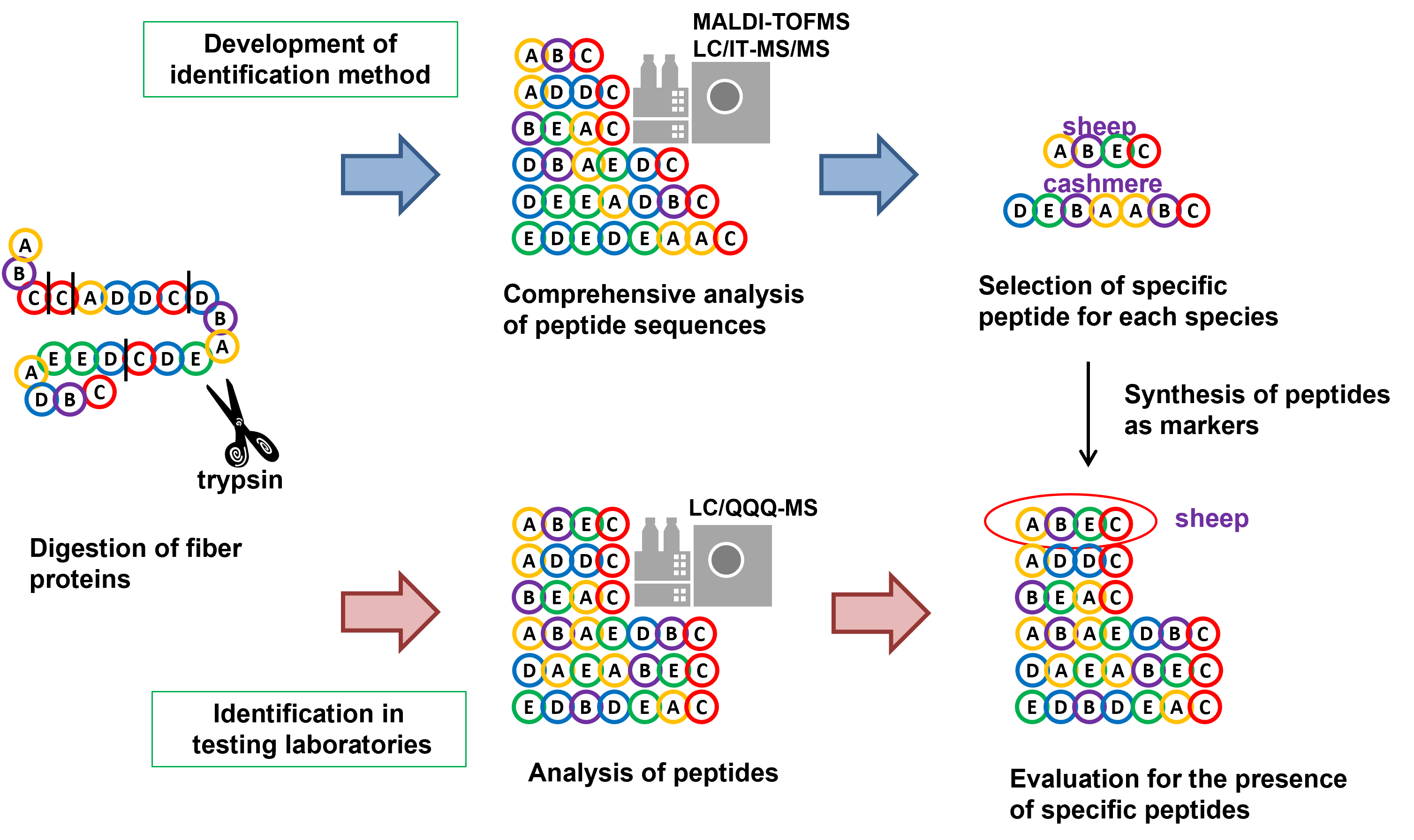
- (4) Calculation of quantitative ratio
- Fibers of cashmere and sheep were blended in various ratios, and were measured by the triple quadrupole LC/MS. The peak areas of peptides for identification had a correlation with the blending ratios as shown in the graph on the right. However, there was 10% or more systematic difference between the measured values and the actual values. This is considered to be mainly due to the difference of the keratin content in two fibers and the difference of the sensitivity of mass spectrometer to two peptides. This therefore indicates that the calibration of each peptide for identification is required in order to calculate the blending rates. The blending ratio of each fiber such as sheep wool (Ovis aries), cashmere (Capra hircus), yak (Bos grunniens), camel (Camelus ferus), alpaca (Vicugna pacos) and angora rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) is computed by determining the corrected values.
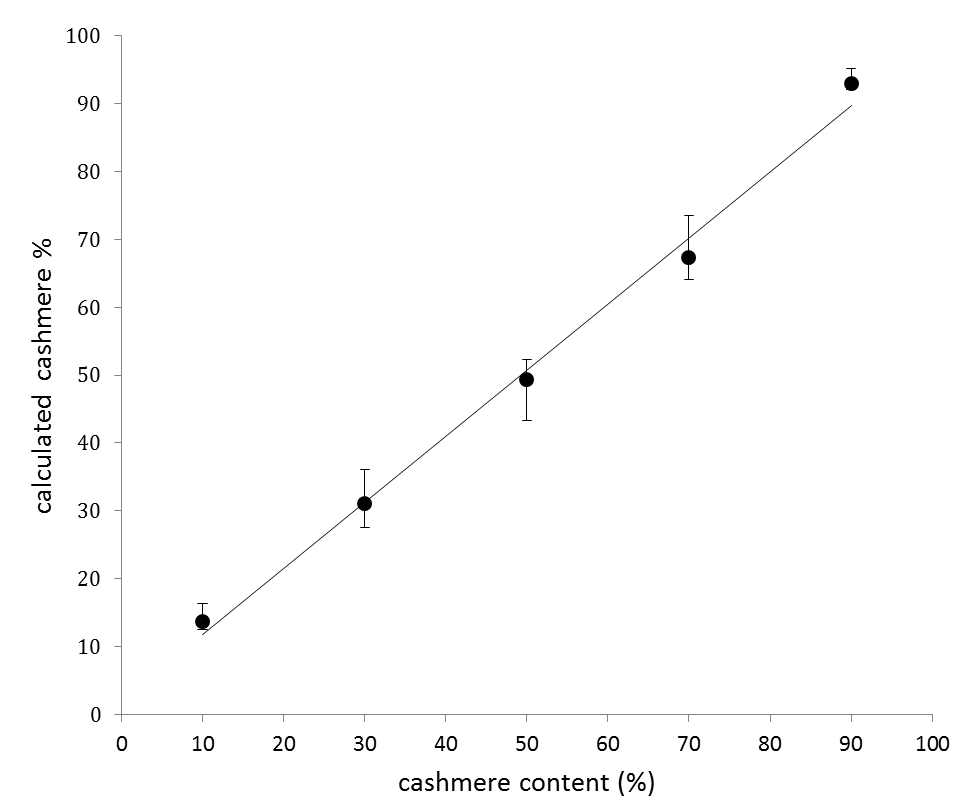
Results of analysis
- This study was presented as follows.
- Annual Meeting of the Society of Fiber Science and Technology, Japan. (2013), 2PA52
- “Identification and quantitative analysis of the cashmere, sheep and yak fibers using the high-speed liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer.”
Kazumi Sasaki, Keiko Nishijima, Hanako Ataku - “Differential Identification and Quantification of Cashmere, Sheep and Yak Fibers in Textiles Using Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry.”
- Hanako Ataku, Keiko Nishijima, Ayumi Mori, Nobuyuki Fujita, and Kazumi Sasaki
- News Release (June 15, 2020)
- New International Standard for Method of Distinguishing Animal Hair Fibers proposed by Japan was issued
- Method for distinguishing cashmere and other high-end animal hair fibers contributing to enhancing fair trade in international markets -
Analytical Instruments
The mass spectrometers used for the analysis are introduced below.
- Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Tandem Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometer (MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS)
- Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer (LIT-MS)
- Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometer (FT-ICR-MS)
- Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (QqQ-MS)
- Single Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (Q-MS)
Contact us
- Biotechnology Evaluation and Development Division, Biological Resource Center, National Institute of Technology and Evaluation
-
Address:2-49-10 Nishihara, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 1510066, Japan MAP
Contact Form


